Monthly Bike Rentals With Zero Deposit
Flexible monthly bike rentals with unlimited kilometers, free maintenance, comprehensive insurance, and complete peace of mind. Experience freedom on two wheels.
4.8/5 from 35,000+ happy riders

Flexible monthly bike rentals with unlimited kilometers, free maintenance, comprehensive insurance, and complete peace of mind. Experience freedom on two wheels.
4.8/5 from 35,000+ happy riders

Years of Trust
Happy Riders
Active Fleet
At Ontrack, quality comes first. That's why we offer only 2-wheelers from trusted OEMs like Honda, Hero, Bajaj and TVS—with zero compromise on reliability.
Every Ontrack bike is serviced at our in-house workshops by experienced technicians, strictly as per OEM standards—so you ride with complete peace of mind.

We offer both EVs and petrol 2-wheelers, so you can ride the way you prefer. Choose from reliable petrol bikes or switch to electric for a greener ride.
EVs also available for weekly rentals!
Perfect for short-term needs, weekend getaways, or trying out electric vehicles.

Ride with complete confidence knowing that our Road Side Assistance team is available round the clock to support you. From sudden breakdowns to unexpected on-road issues, we’ve got you covered.
Fast help, minimal downtime, and zero hassle.
Whether it’s a flat tyre, battery issue, or mechanical trouble, our team ensures quick resolution so you can get back on the road safely and without stress.
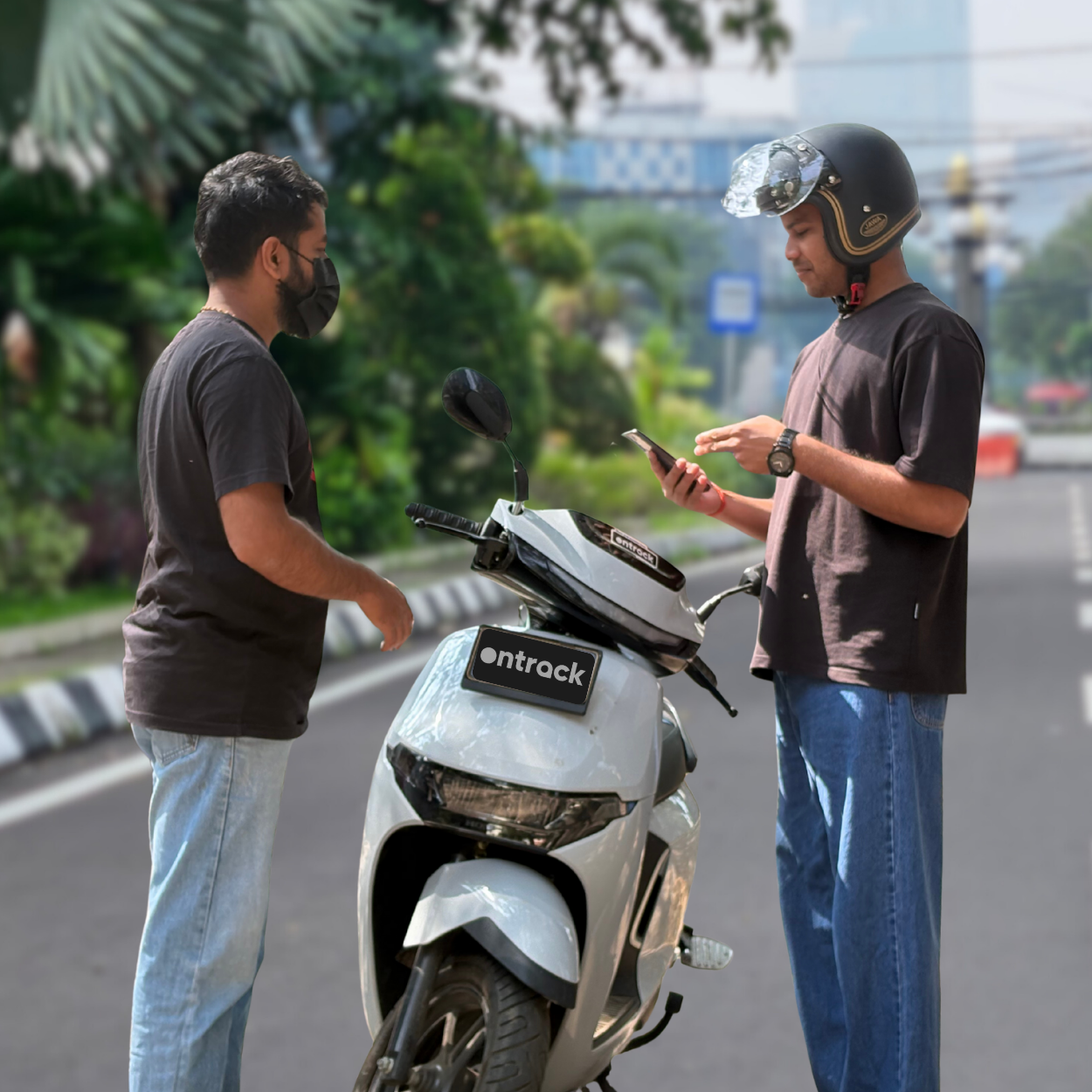

Designed for the modern workforce. We eliminate the hassles of bike ownership while providing premium benefits that put riders first.
Simply said, we trust you.
Pay only the rental amount and start riding. No hidden charges or large deposits required.
One Free Service Per Month
Regular maintenance included. Additional service available for just ₹450 - well below market rates.
Fully Protected Rides
Ride with complete peace of mind. All our bikes come with comprehensive insurance coverage.
No Meter Watching
Ride as much as you want without worrying about extra kilometer charges. Explore without limits.
True Flexibility
No minimum commitment beyond the first month. Rent monthly and cancel anytime with notice.
Breakdown Support
Partnered with multiple RSA providers for round-the-clock emergency support across Bengaluru.
Join thousands of satisfied riders in Bengaluru.
Start Your Ride TodayRewards by Ontrack makes every ride more rewarding. Pay through the Ontrack App and earn 10% back as Ontrack Points on every payment.
Use your points to rent a bike or while extending an existing booking—pay up to 10% of your bill using points.
Earn 10% back as points on every payment made on the app.
Refer friends and earn bonus points every time they rent a bike.

Download the Ontrack app to book rides, schedule maintenance, make payments, and get 24/7 support right from your pocket.
Looking for a top bike rental in Bangalore without worrying about distance limits? Ontrack Bike Rentals is one of the very few bike rental services in Bangalore that offers unlimited kilometers on rentals. Whether you are commuting daily, exploring the city, or heading out on a weekend ride, you can ride freely without calculating per-kilometer costs or hidden charges.
Ontrack offers some of the lowest bike rental prices in Bangalore, making it the best choice for budget-friendly travel. Our pricing is transparent and designed to suit everyone—from students and working professionals to long-term residents. With Ontrack, you always get the best price for bike rentals in Bangalore without surge pricing or last-minute cost surprises.
Unlike other bike rental services that offer only daily or monthly rentals, Ontrack is one of the only bike rental platforms in Bangalore to provide flexible weekly rental plans. These plans are perfect for short-term needs such as interviews, project work, business travel, or temporary stays in the city, giving you maximum flexibility at minimum cost.
Traveling around Bangalore does not have to be expensive. Ontrack provides bike rentals at very affordable rates, making two-wheeler rentals accessible to everyone. Compared to cabs and autos, renting a bike in Bangalore with Ontrack helps you save significantly on daily travel expenses while enjoying complete freedom of movement.
Cabs in Bangalore often come with high fares, long waiting times, and frequent booking cancellations, especially during peak hours. Public transport can be crowded and unpredictable. With an Ontrack bike rental, you can skip the traffic, park easily, and reach your destination on time—every time—without paying extra for distance or delays.
For short-distance travel and everyday use, Ontrack offers scooter rentals in Bangalore at some of the lowest prices in the city. Renting a scooty in Bangalore with Ontrack is ideal for grocery runs, office commutes, house hunting, and quick errands. Our scooters are easy to ride, fuel-efficient, and available with unlimited kilometers.
Owning a bike in Bangalore comes with maintenance costs, insurance hassles, and depreciation. With Ontrack Bike Rentals, you avoid all these worries. We take care of maintenance and servicing, ensuring that every bike is in excellent condition. You simply choose a bike, ride as much as you want, and pay less—no ownership stress involved.
If you are searching for a reliable, affordable, and flexible bike rental service in Bangalore, Ontrack is the right choice. With unlimited kilometers, the best prices, and exclusive weekly rental plans, Ontrack Bike Rentals gives you the freedom to move around Bangalore on your own terms.